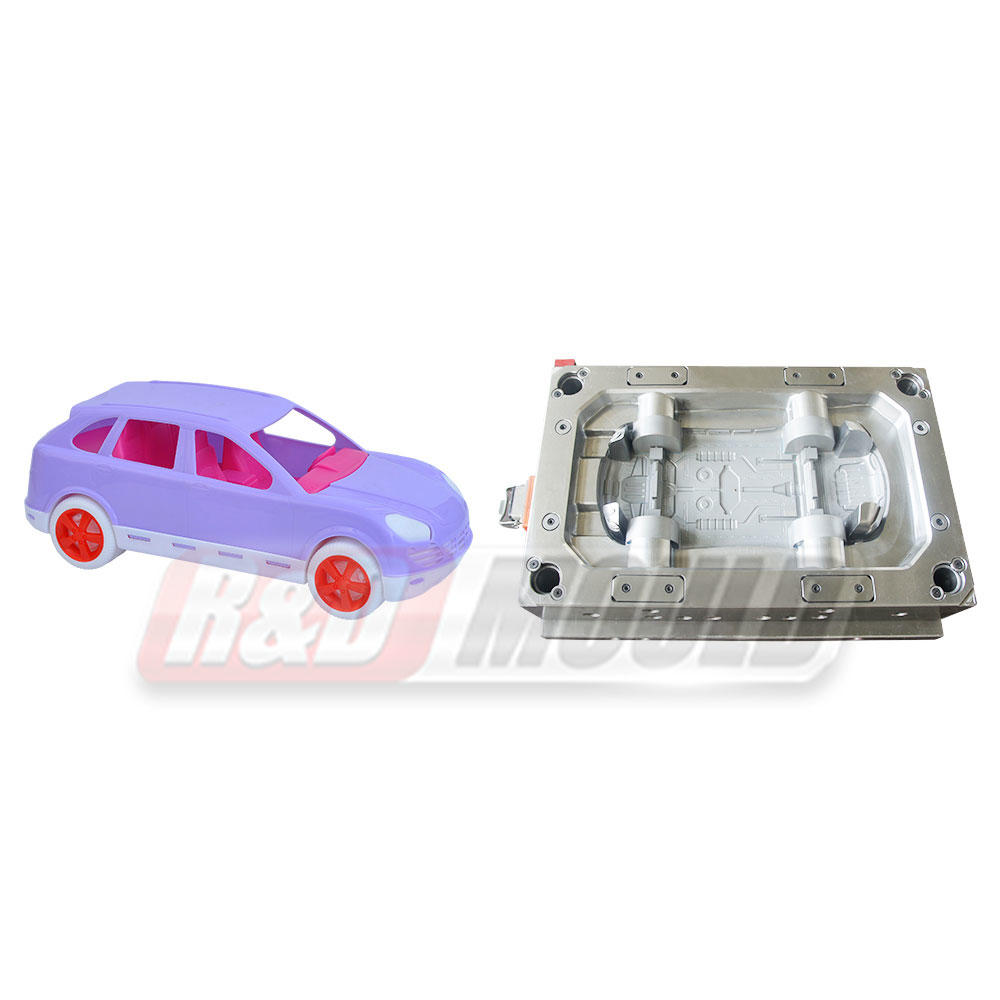
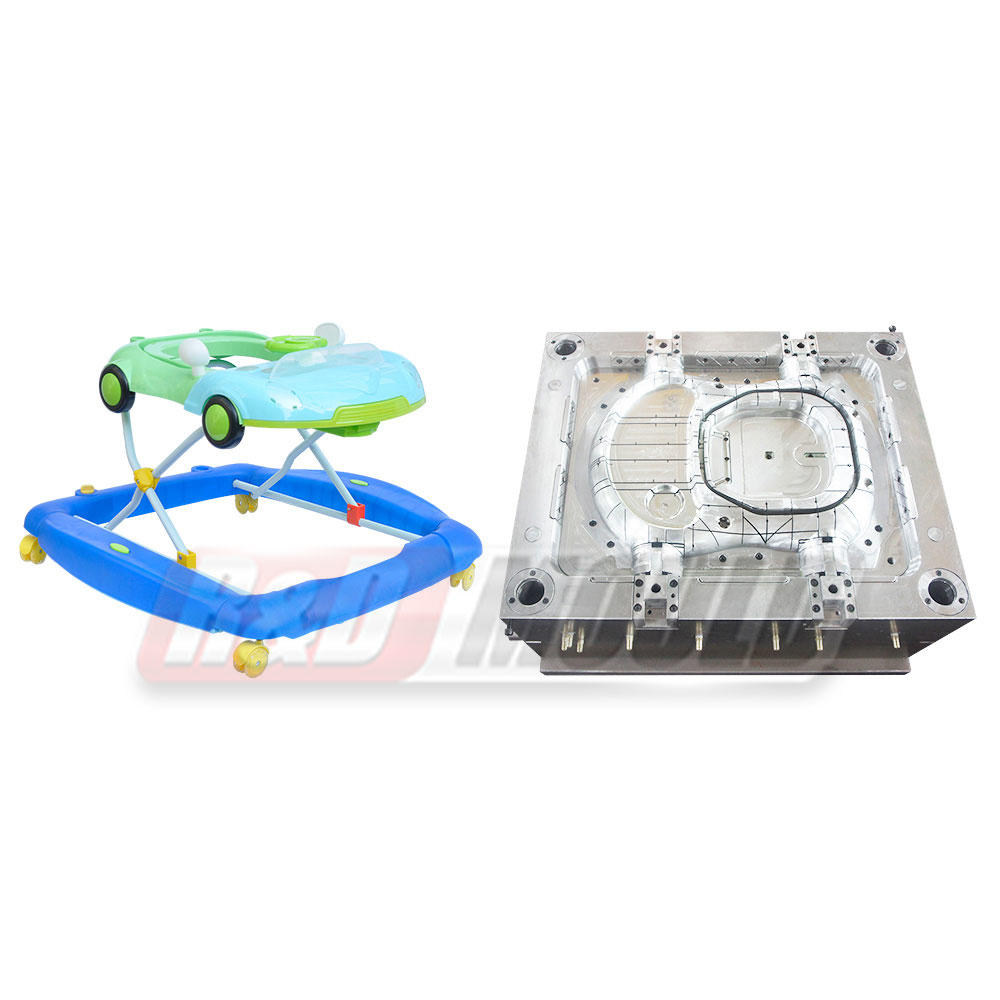
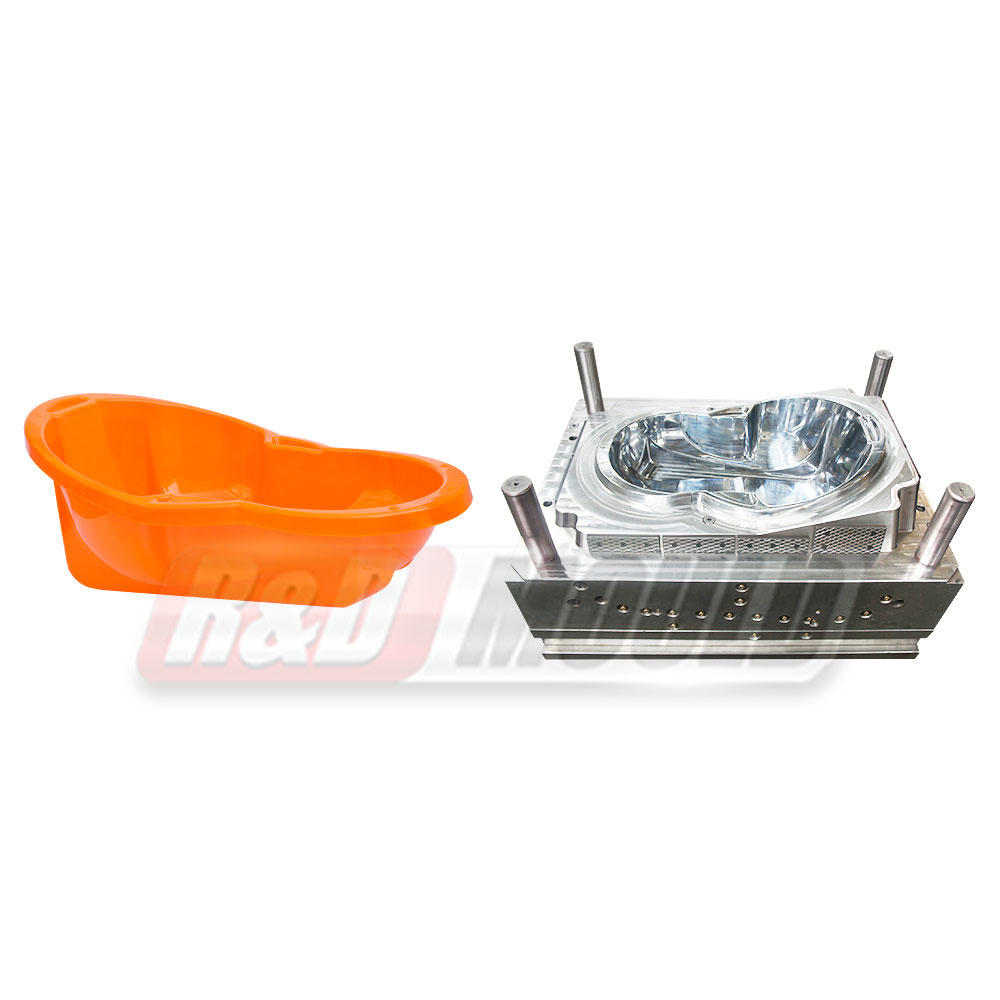
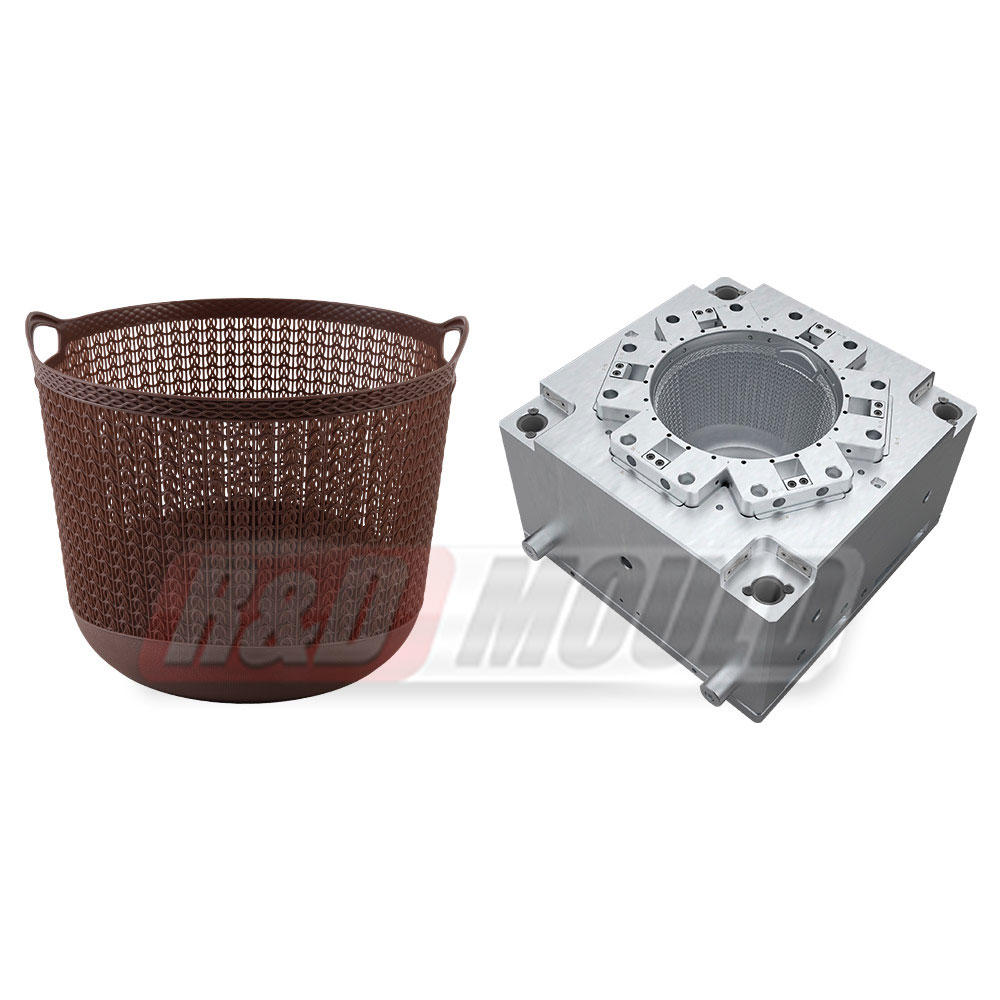
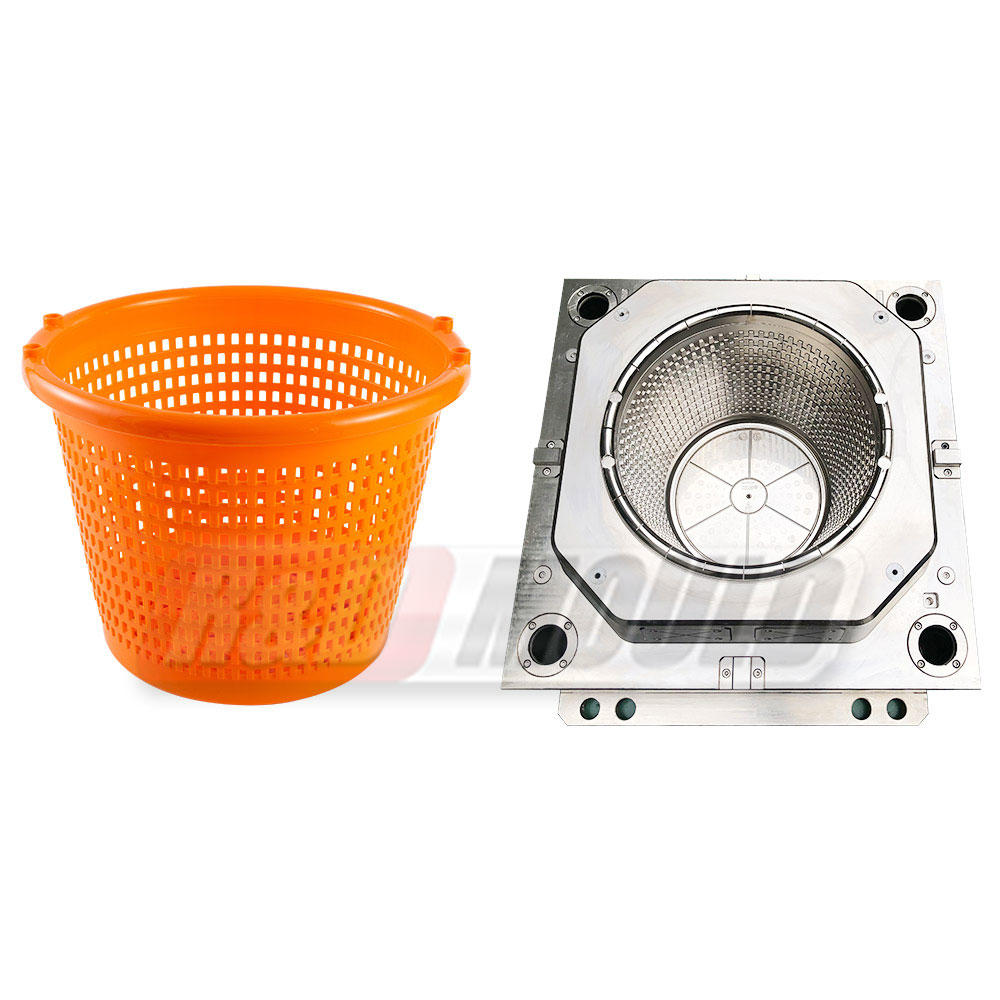
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify into the desired shape. The process is often used for producing plastic parts and products, but it can also be applied to a range of materials, including metals and ceramics. Here's how the process works:
Material Preparation: The raw material, usually in the form of pellets or granules, is loaded into a hopper, where it is heated and melted. The material can be a thermoplastic, thermosetting plastic, or a variety of other materials.
Injection: The molten material is injected into a mold cavity using a reciprocating screw or a plunger. The mold is usually made of steel and precision-machined to the exact specifications of the desired product.
Cooling: Once the material is injected into the mold, it is allowed to cool and solidify. The cooling process is crucial for ensuring the final product's structural integrity and quality.
Ejection: After the material has solidified, the mold opens, and the newly formed part is ejected from the mold cavity. The process is repeated for each new part.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding is highly versatile when it comes to the materials that can be used. Some of the most common materials include:
Thermoplastics: These materials, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, can be melted and re-melted, making them suitable for recycling and multiple manufacturing cycles.
Thermosetting Plastics: Once set, these materials cannot be remelted. Examples include phenolic and epoxy resins, which are known for their heat resistance and durability.
Elastomers: Elastomeric materials, like silicone and rubber, can be used to produce flexible and resilient products.
Metals and Ceramics: Injection molding can also be applied to produce metal and ceramic parts, offering precision and consistency in manufacturing.
Applications of Injection Molding
The versatility of injection molding lends itself to a wide range of applications. Some common industries and products produced using this method include:
Automotive: From dashboard components to bumpers, injection molding is used to create various parts within the automotive industry.
Electronics: Plastic casings for electronic devices, such as smartphones, are often manufactured through injection molding.
Medical Devices: Precision and consistency are critical in the medical industry, making injection molding the method of choice for producing items like syringes and medical equipment components.
Packaging: Many plastic bottles, containers, and caps are created using injection molding, ensuring product protection and safety.
Consumer Goods: Items like toys, kitchen appliances, and even everyday items like toothbrushes are produced through injection molding.
Aerospace: Injection molding is used to manufacture lightweight and durable components for aircraft and spacecraft.
Sustainability and Injection Molding
In recent years, sustainability has become a significant concern in manufacturing. Injection molding can contribute to sustainable practices in several ways:
Recycling: Many thermoplastics used in injection molding are recyclable, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Reduced Material Waste: The precision of injection molding minimizes material waste compared to other manufacturing methods.
Energy Efficiency: The process is energy-efficient, as it requires less power to heat and cool materials compared to other techniques.




 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français