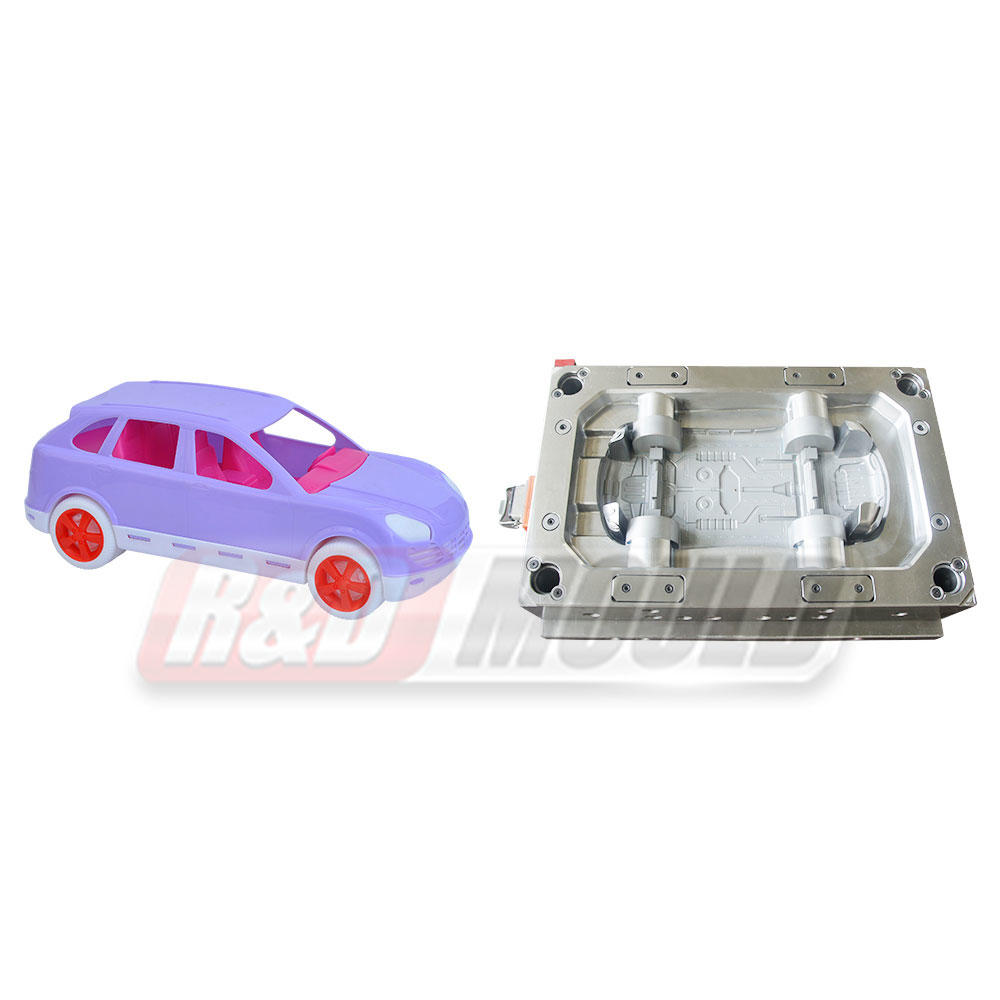
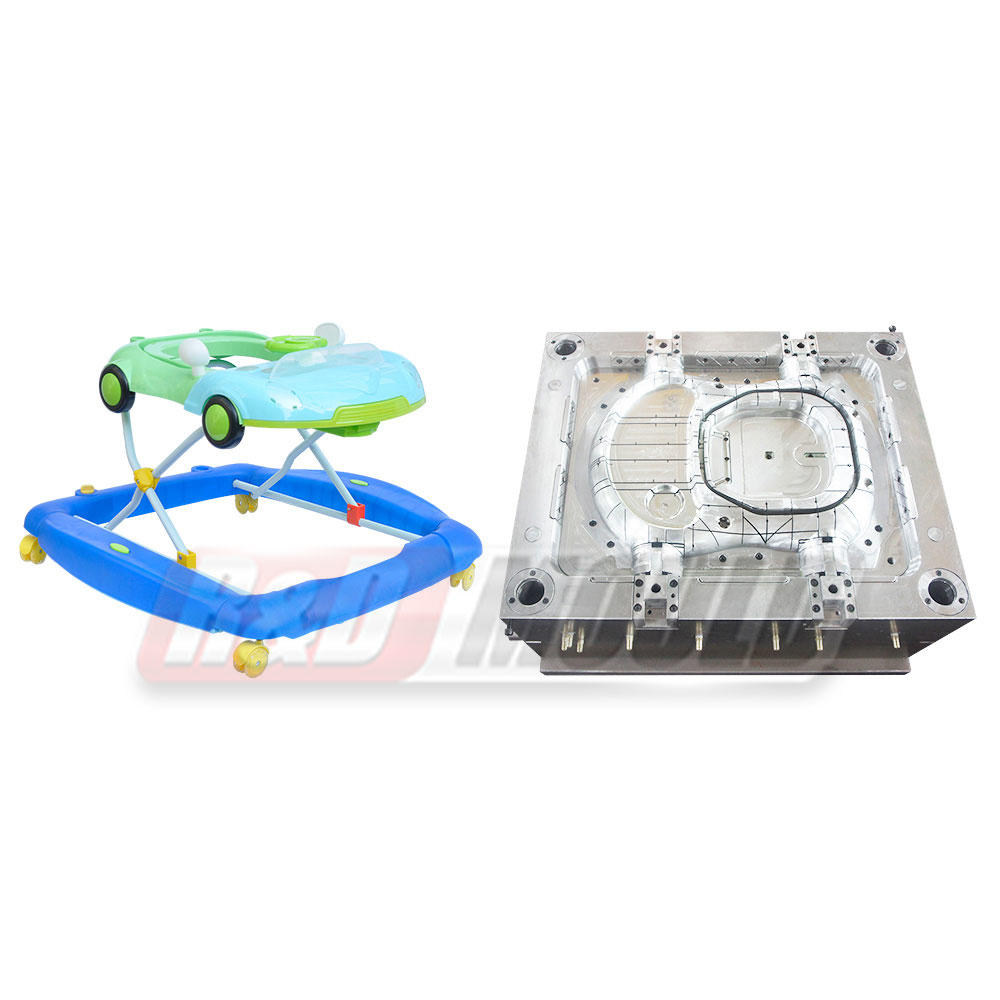
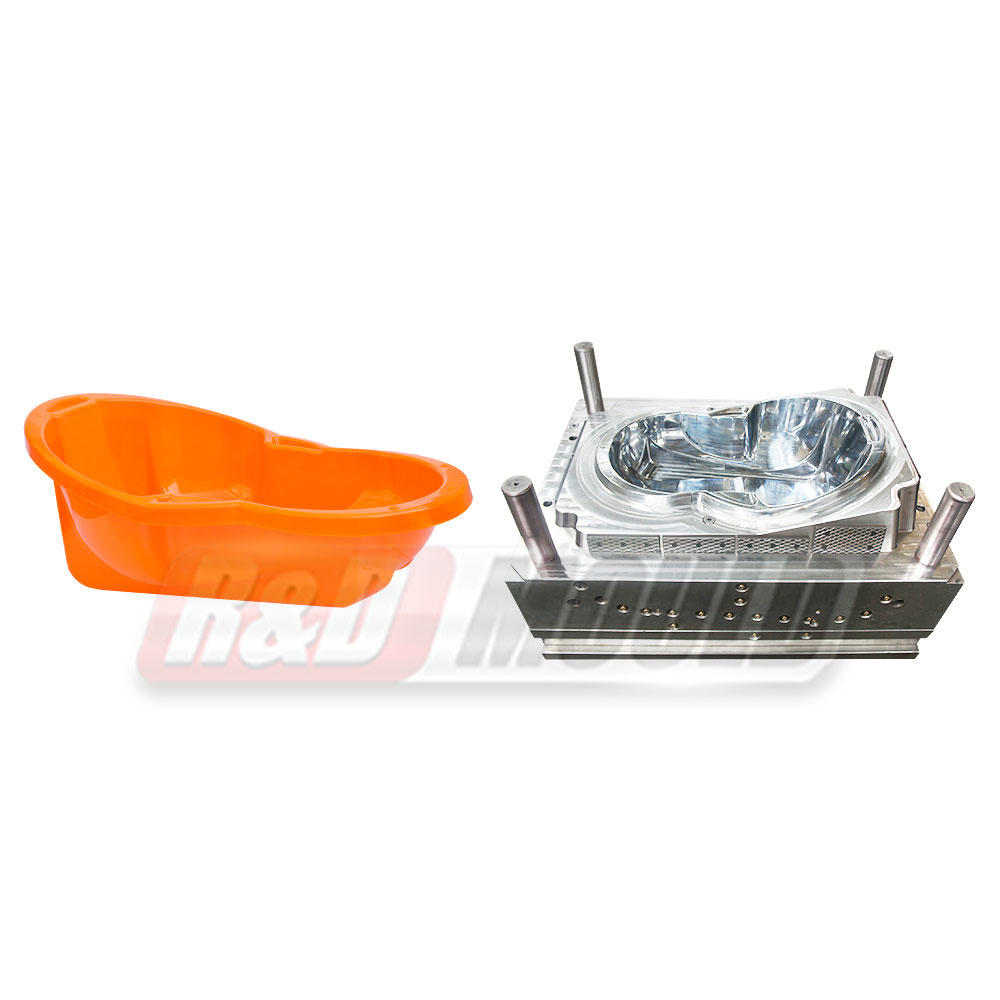
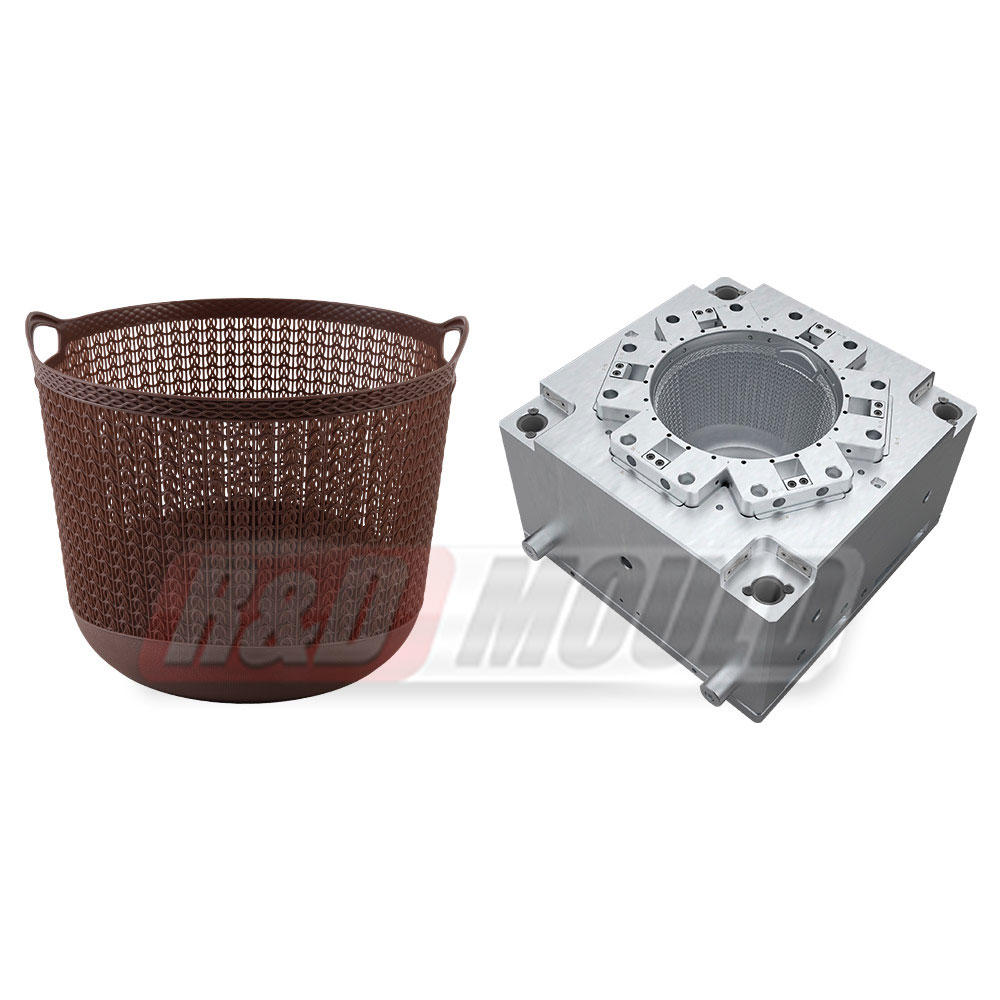
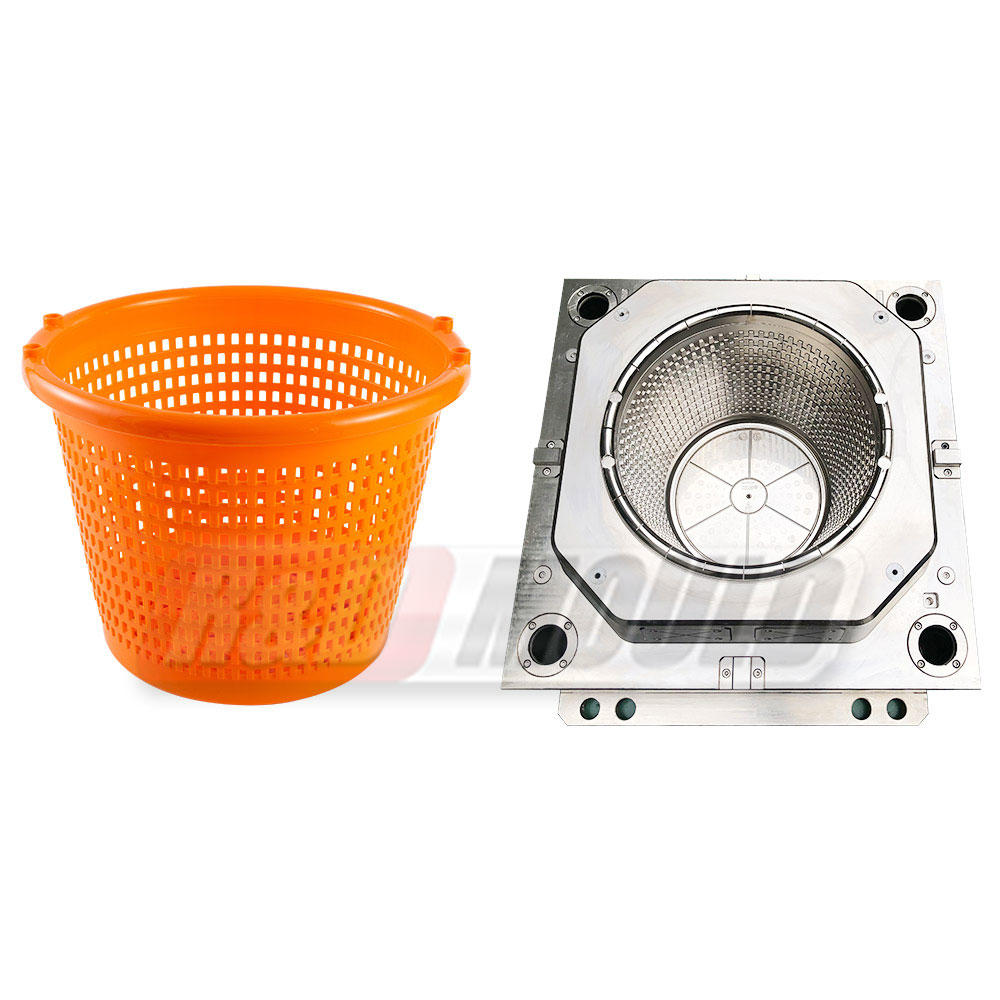
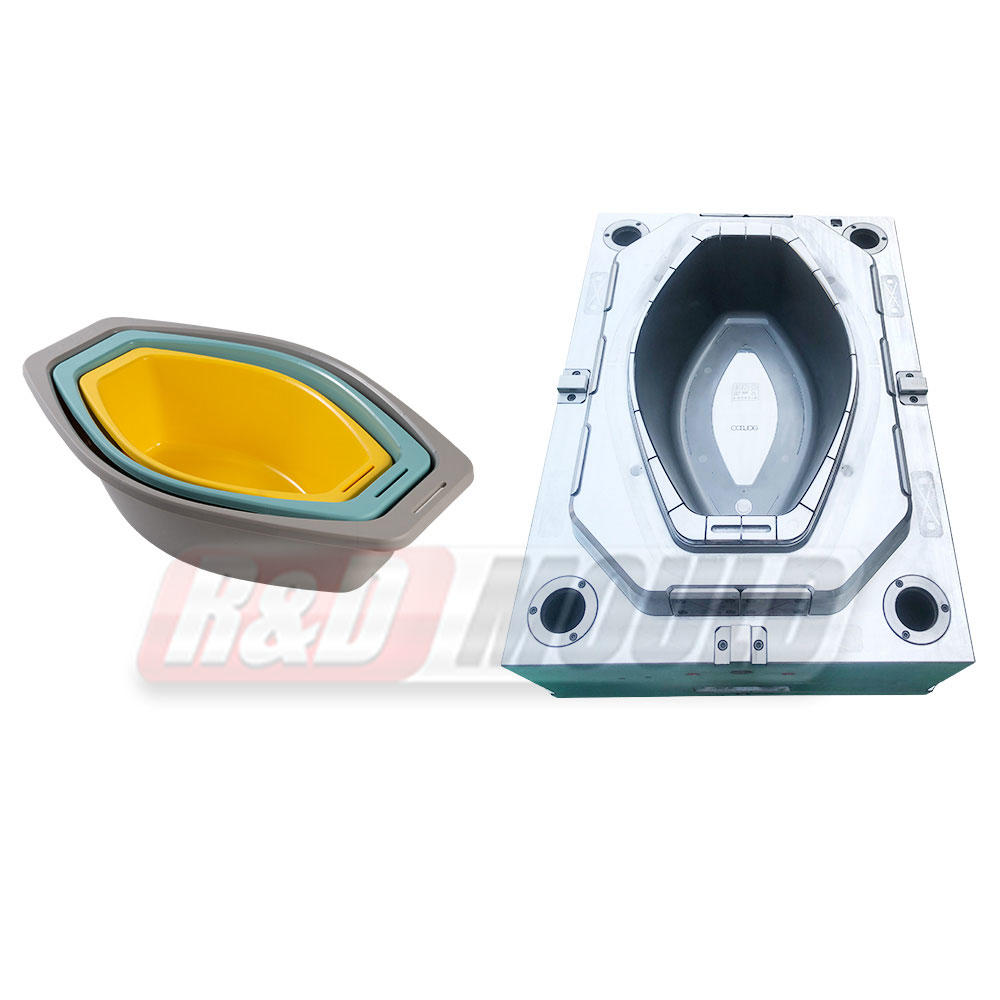
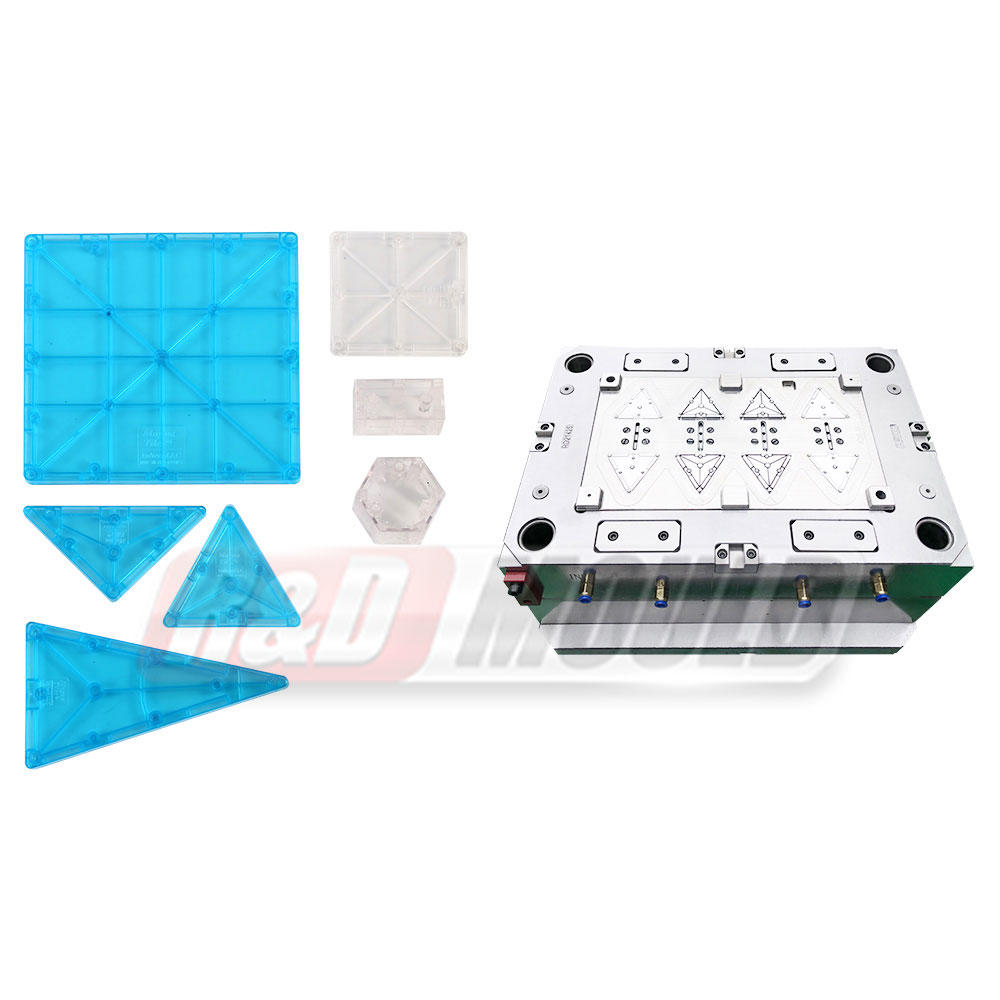
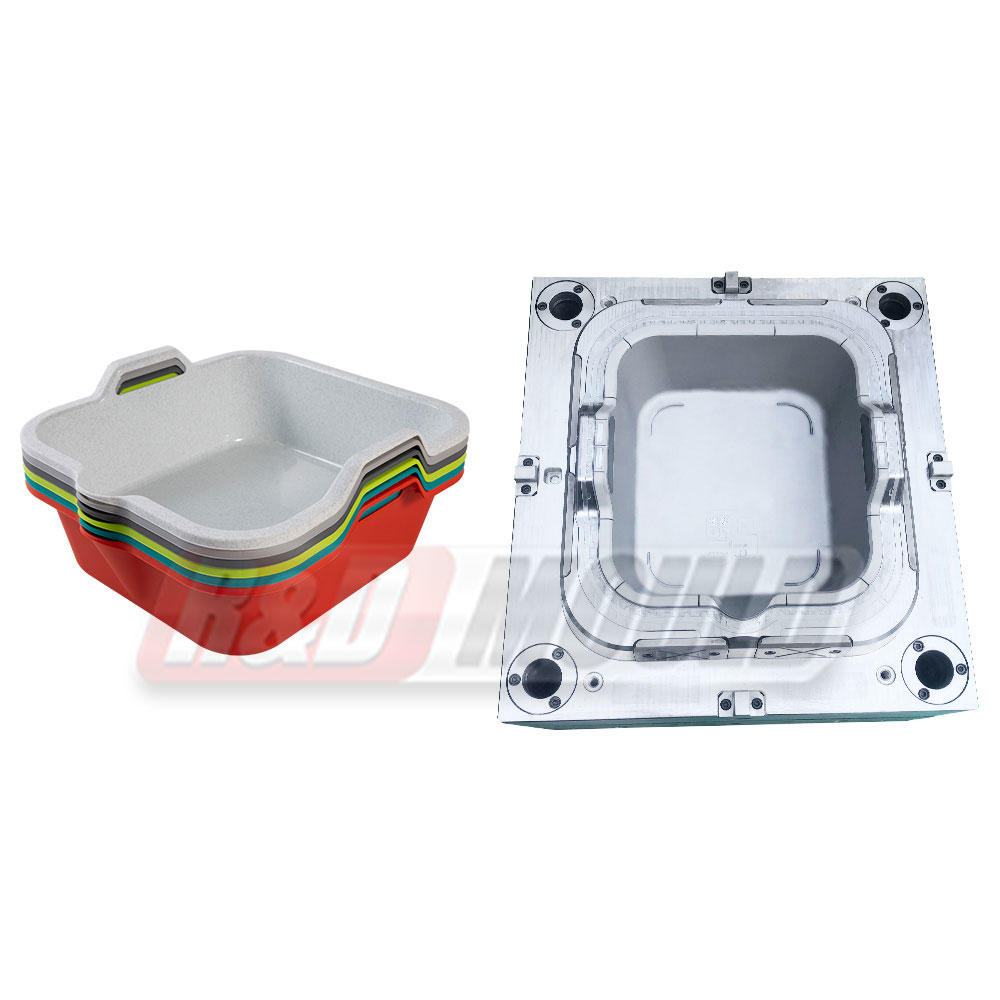
At the heart of plastic injection molding lies the mold itself. These molds are precision-engineered tools designed to shape molten plastic material into desired forms. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity under high pressure, allowing it to cool and solidify, ultimately producing the intended product.
These molds are typically made from metals, such as steel or aluminum, due to their durability and ability to withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the injection molding process. Molds come in various types, including single cavity molds, multiple cavity molds, family molds, and complex molds capable of producing intricate designs and shapes.
The Significance of Injection Molding Molds in Manufacturing
The versatility and efficiency of plastic injection molding molds make them integral to the manufacturing industry. Their ability to produce high volumes of consistent, high-quality parts with minimal waste has made them indispensable in numerous sectors, including automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer goods, and more.
injection molding molds offer unparalleled precision, enabling manufacturers to create intricate geometries and complex features that would be challenging or impossible to achieve using other manufacturing techniques. This precision contributes to the production of products with tight tolerances and exact specifications, meeting the stringent demands of various industries.
Diverse Applications and Innovations
The applications of plastic injection molding molds span a wide spectrum of industries and products. In the automotive sector, these molds are utilized to create components ranging from interior panels and dashboards to intricate engine parts. Similarly, in the medical field, injection molding molds play a pivotal role in producing medical devices, syringes, and components for diagnostic equipment.
The continuous advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies have spurred innovations in injection molding molds. Enhanced materials, such as high-performance alloys and coatings, have improved the durability and lifespan of molds, allowing for longer production runs and reducing downtime for maintenance.
the integration of technologies like computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and 3D printing has revolutionized mold design and prototyping. These advancements enable quicker iterations, reduced lead times, and enhanced customization, facilitating the creation of molds tailored to specific product requirements.
Environmental Considerations and Future Prospects
While plastic injection molding has undoubtedly revolutionized manufacturing, concerns regarding environmental sustainability persist. The reliance on plastic materials and the energy-intensive nature of molding processes have raised questions about waste generation and energy consumption.




 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français