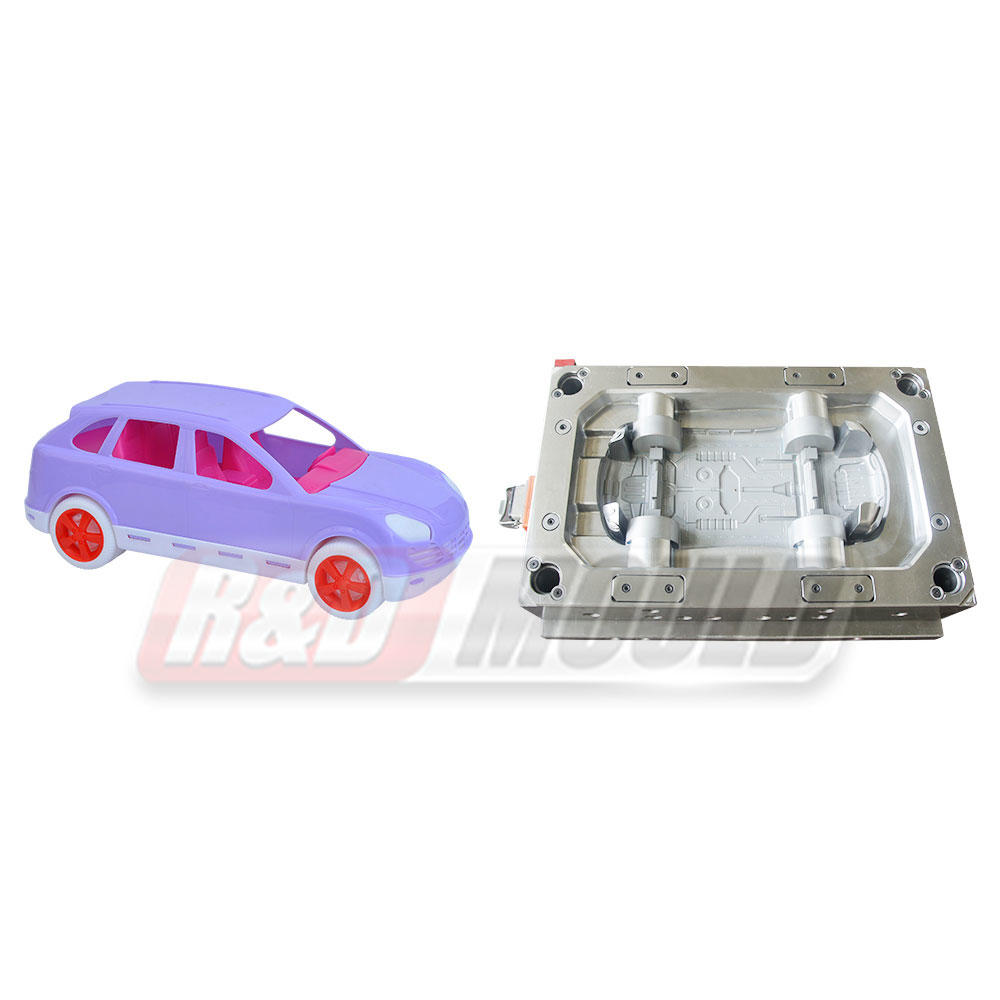
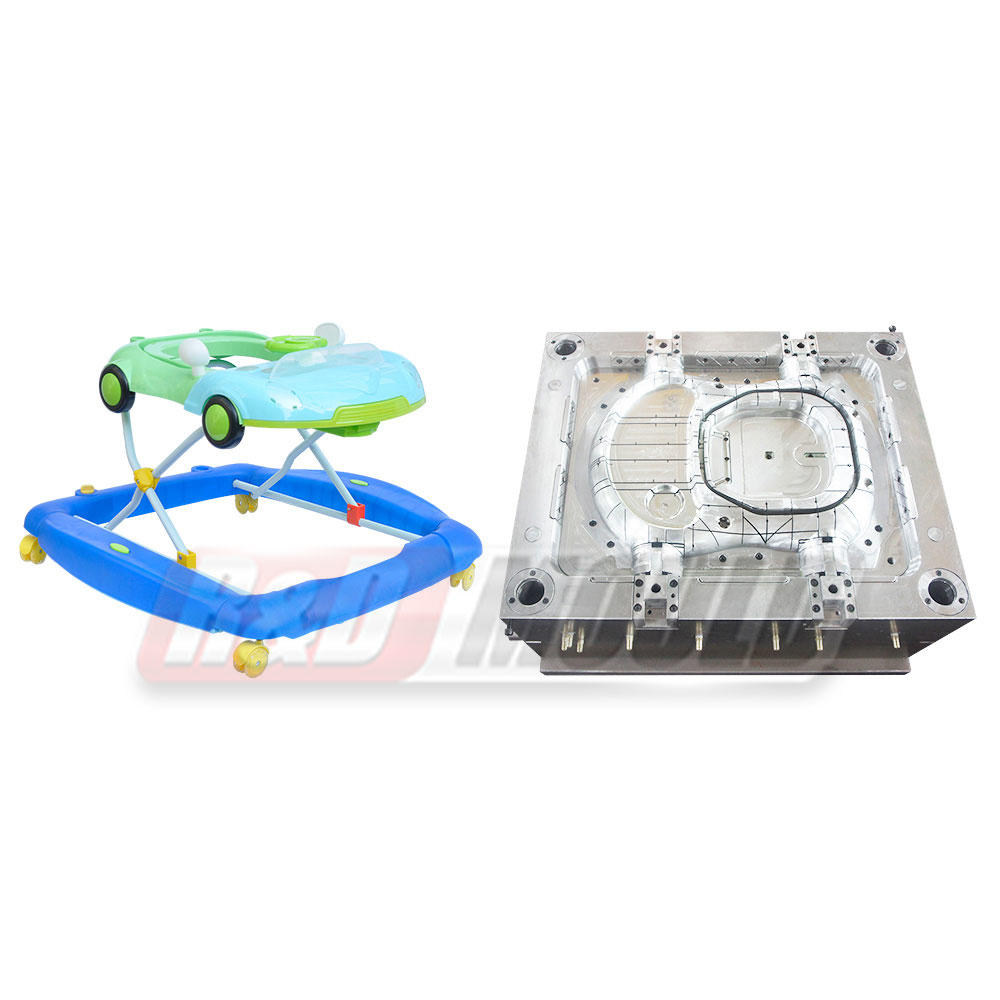
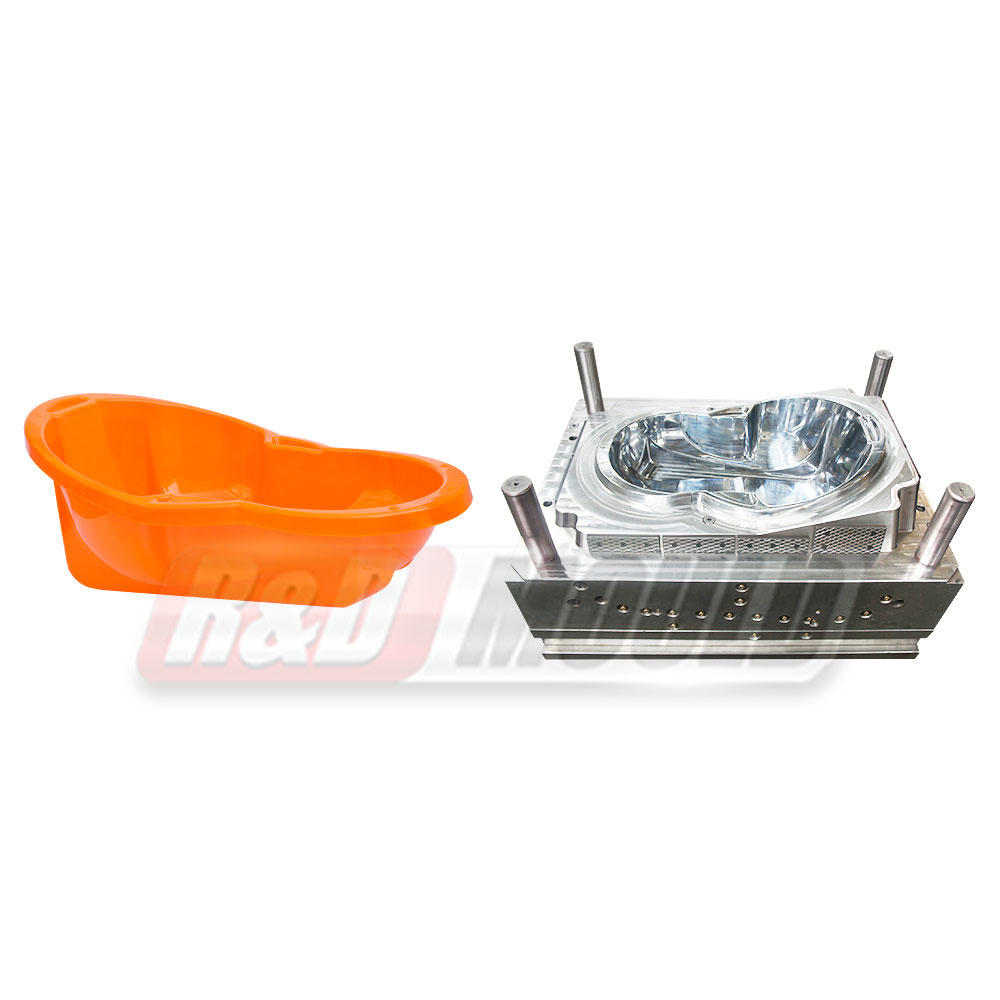
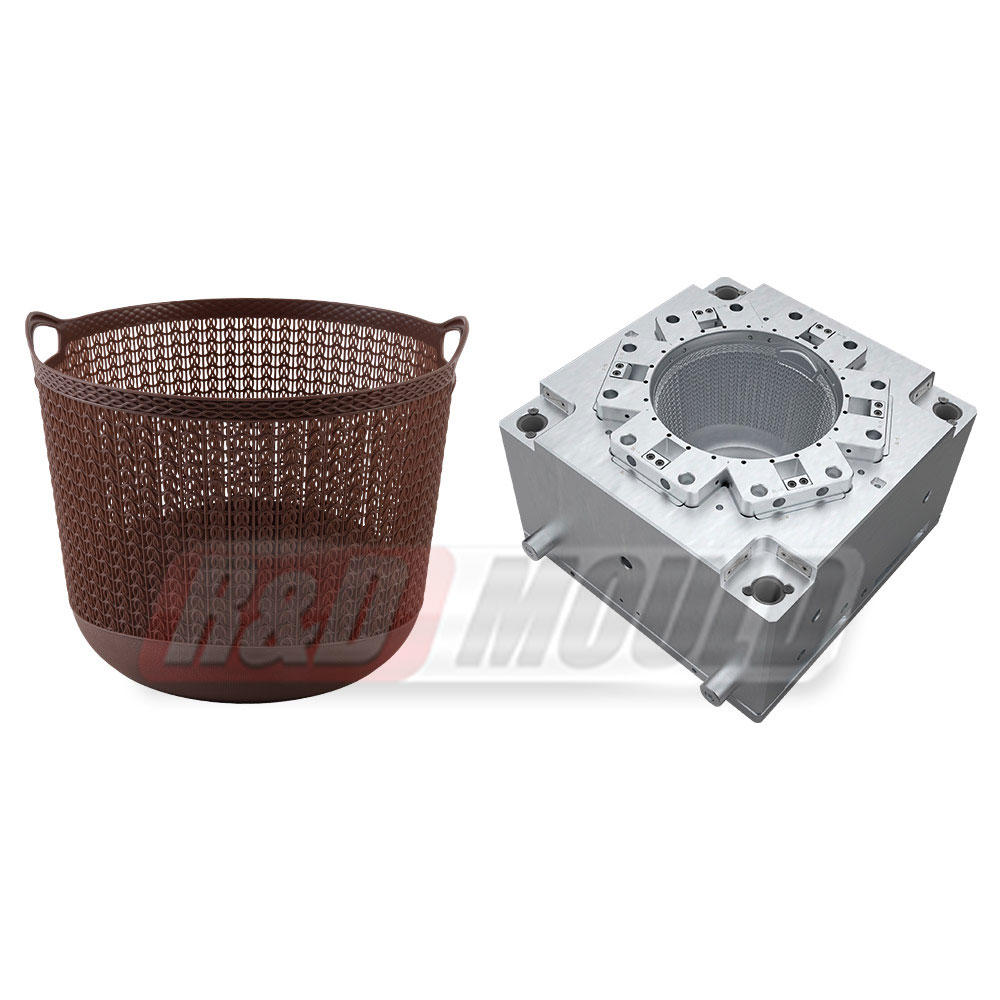
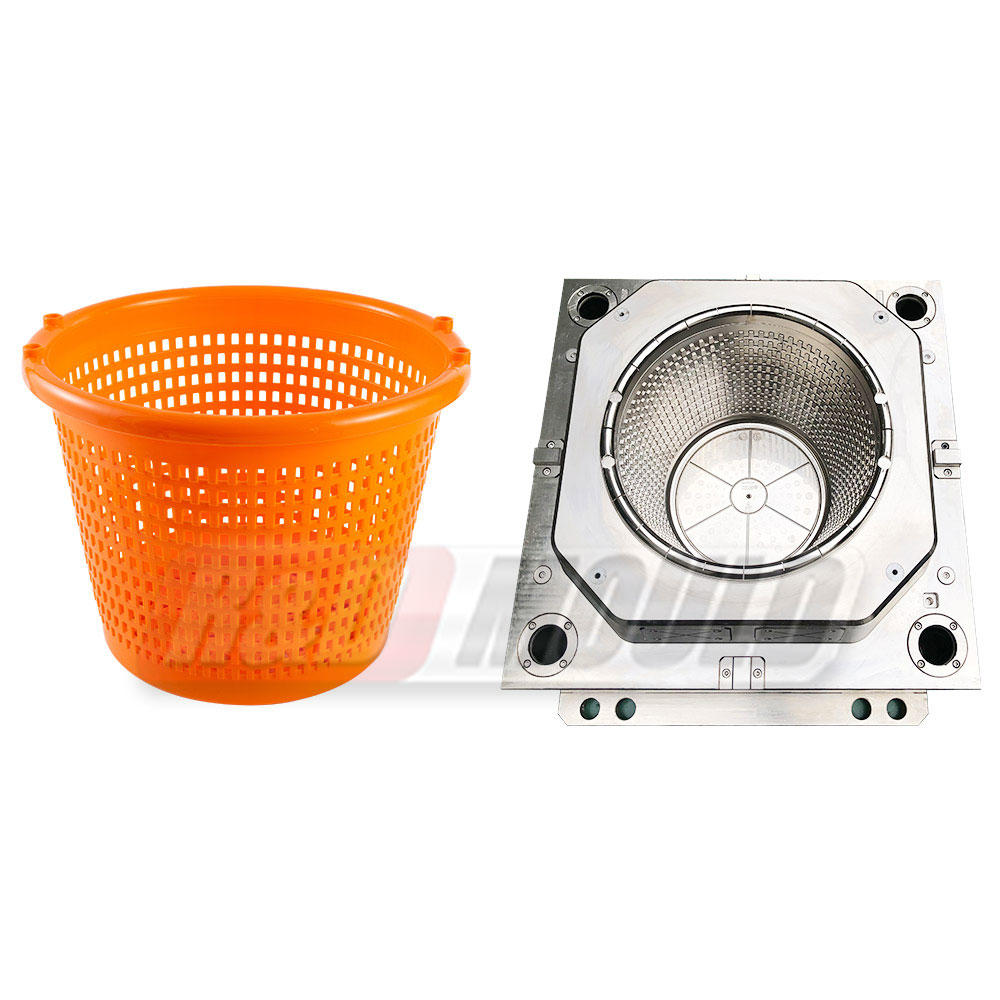
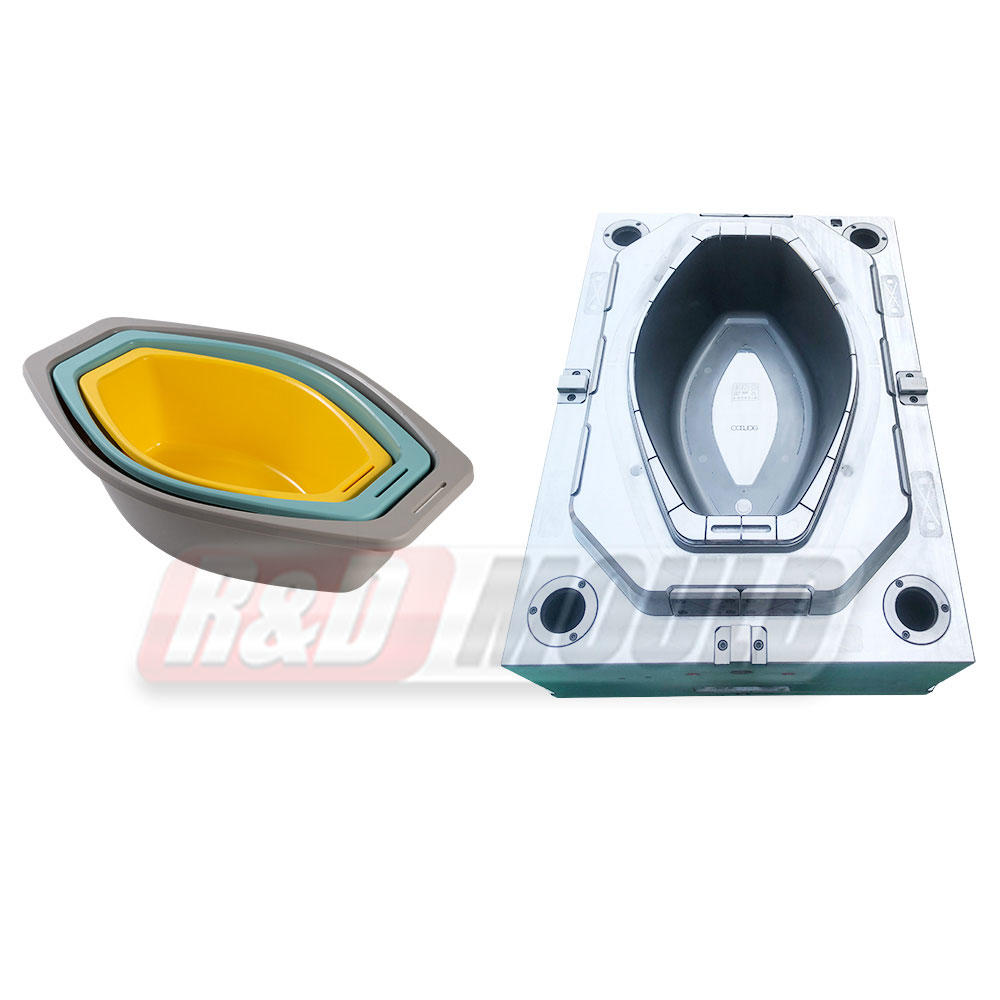
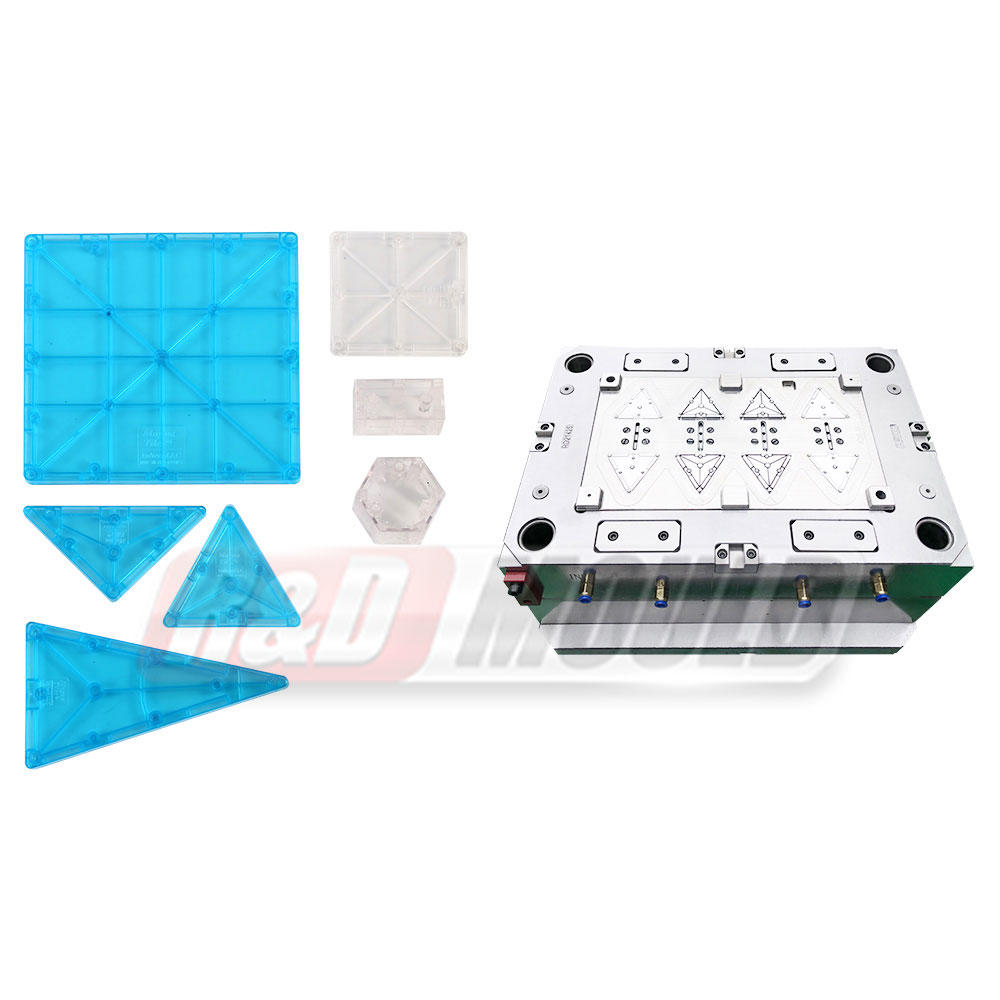
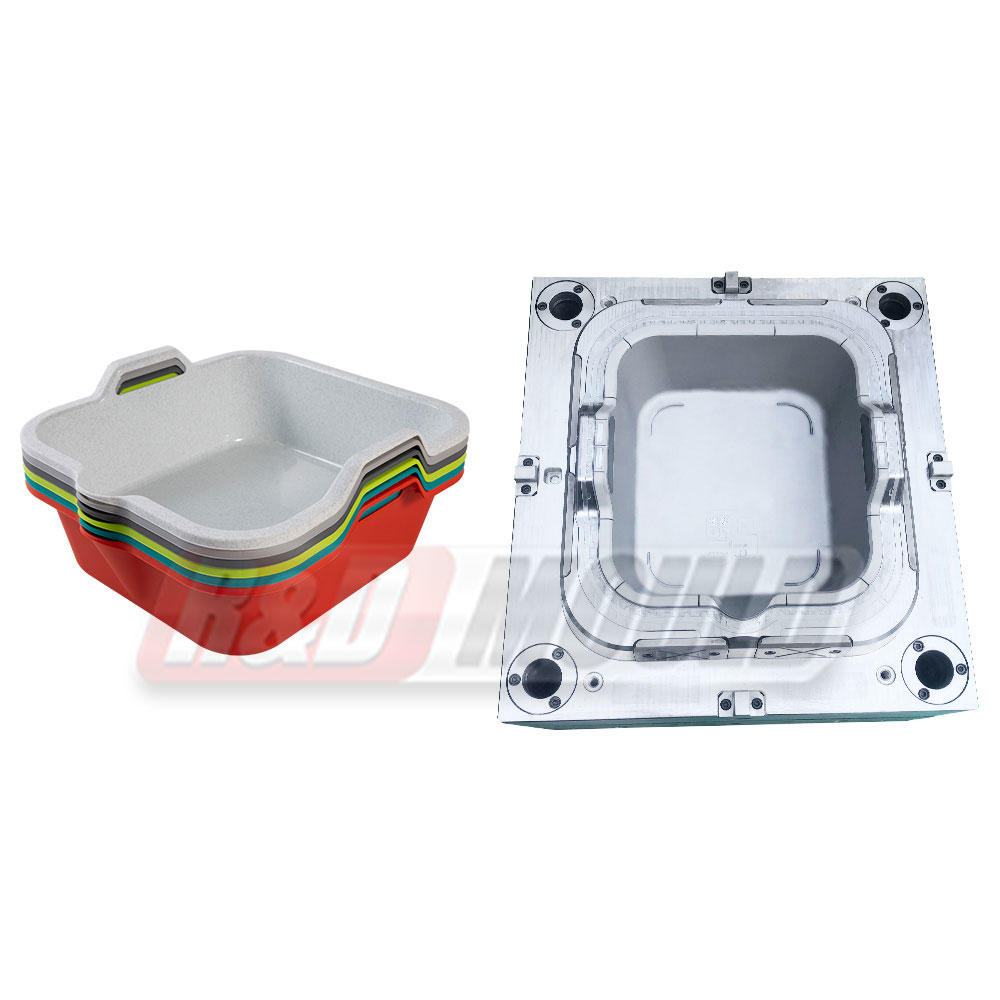
Blow molding is a manufacturing process that involves shaping hollow plastic objects by inflating them with compressed air. It is a highly efficient and cost-effective method for producing large quantities of plastic products with consistent quality. Blow molding allows for the creation of complex shapes, intricate designs, and varying sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
2. The Blow Molding Process
The blow molding process can be divided into three main types: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding. Here's a brief overview of each:
a. Extrusion blow molding: This is the most common form of blow molding. It begins with the melting of plastic resin, which is then extruded into a tube called a parison. The parison is clamped into a mold, and compressed air is blown into it, expanding it to conform to the shape of the mold. The plastic is cooled, solidified, and ejected as a finished product.
b. Injection blow molding: This process starts with the injection of molten plastic into a preform, which is then transferred to a blow mold. The preform is inflated with air, taking the shape of the mold. Once cooled, the product is removed from the mold. Injection blow molding is commonly used for producing small bottles and containers.
c. Stretch blow molding: This technique is primarily used for producing PET (polyethylene terephthalate) bottles. It begins with the injection molding of a preform, which is then reheated and stretched in the axial direction. Compressed air is blown into the stretched preform, expanding it to the desired shape.
3. Applications in Various Industries
Blow molding finds extensive application across diverse industries, catering to a wide array of needs. Some notable industries that heavily rely on blow molding include:
a. Packaging: Blow molding is widely used in the packaging industry to manufacture bottles, containers, jars, and other packaging solutions for food, beverages, personal care products, and household chemicals.
b. Automotive: Blow molding is used to produce components such as fuel tanks, air ducts, bumpers, and reservoirs in the automotive industry. Its lightweight yet durable nature makes it an ideal choice for automotive applications.
c. Medical: Blow molding plays a crucial role in producing medical devices, such as IV bags, drug containers, respiratory masks, and laboratory equipment, ensuring hygienic and sterile solutions.
d. Industrial: Blow molding is employed in the industrial sector for manufacturing drums, storage tanks, and large containers used in transportation, agriculture, and chemical storage.




 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français